Blog
Is Mongolia part of China?
Mongolia and China, two neighboring nations in Asia, have long been intertwined through history and culture. Despite these close connections, the relationship between the two nations and their territories isn’t always understood clearly. A common question that arises is: “Is Mongolia part of China?” To address this question, we need to delve into a bit of historical and geographical context.
Understanding Mongolia’s Sovereignty
Founded as an independent nation in 1921, Mongolia, officially known as the Mongolian People’s Republic, is a sovereign state located in East and Central Asia. Flanked by Russia to the north and China to the south, east, and west, Mongolia occupies a strategically significant location in Asia.
Mongolia’s separation from the Qing Dynasty in 1921 marked its transformation into an independent nation, a status acknowledged worldwide. This was a significant turning point in its history, one that emphasized Mongolia’s distinct identity, separate from China. Despite a turbulent past, Mongolia has remained steadfast in its national autonomy, even as it underwent various political transformations.
Internationally, Mongolia’s sovereignty is well-recognized. The country is a member of the United Nations and maintains diplomatic relations with numerous countries globally. As a parliamentary republic, Mongolia has its own constitution, government structure, national flag, and anthem, underscoring its independent status.
Inner Mongolia (South Mongolia) vs Outer Mongolia
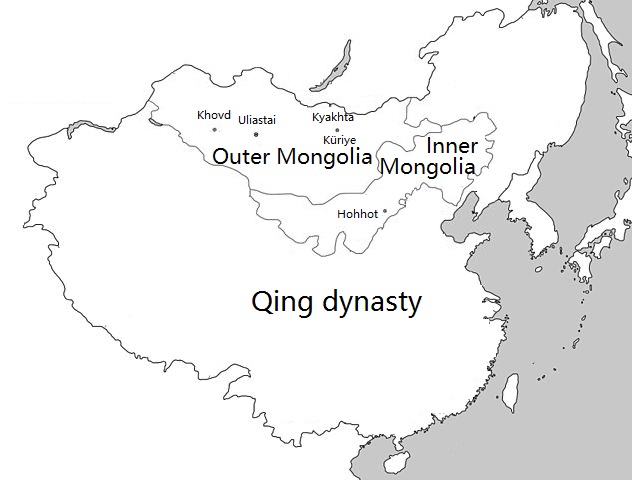
To understand the complex relationship between Mongolia and China, it’s crucial to comprehend the difference between Inner Mongolia and Outer Mongolia.
Inner Mongolia (South Mongolia)
Inner Mongolia, also known as South Mongolia, is an autonomous region of China. It is located on China’s northern border, just south of Mongolia. Despite its name, Inner Mongolia is not part of the independent nation of Mongolia. It is home to a substantial Mongolian population and features a blend of Chinese and Mongolian cultures.
The Chinese government grants Inner Mongolia a degree of autonomy, meaning it can govern itself in certain aspects. However, it ultimately falls under China’s jurisdiction, and its official policies align with those of the Chinese government.
Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia is the term historically used to refer to what we know today as Mongolia. The term “Outer” was used to differentiate it from Inner Mongolia when both regions were part of the Qing Dynasty. After Mongolia gained independence in 1921, the term became less frequently used, as the country established its own national identity distinct from China.
Outer Mongolia or simply Mongolia, is a fully sovereign nation. It has its own government, economic systems, and social structures. Although it has historical and cultural ties with Inner Mongolia, the political distinction between the two is clear.
Cultural Difference Between Inner Mongolia and Outer Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, being an autonomous region within China, manifests a unique blend of Mongolian and Chinese cultures. The Mongolian tradition is deeply rooted in a nomadic lifestyle, reflected in various cultural aspects such as music, dance, traditional sports, and cuisine.
However, these traditions have been influenced significantly by the dominant Han Chinese culture due to centuries of interaction and integration. Mandarin Chinese is widely spoken, alongside Mongolian, and the education system and public life are largely aligned with China’s norms and policies. Additionally, Inner Mongolia has seen an influx of Han Chinese settlers over the years, which has further diluted the distinct Mongolian cultural identity.
In contrast, Outer Mongolia, or the independent nation of Mongolia, has managed to retain a stronger adherence to traditional Mongolian culture, owing to its sovereign status. The Mongolian language, based on the Cyrillic script, is the official language, and nomadic traditions remain central to the nation’s cultural identity. Traditional Mongolian customs, such as Naadam, a sports festival featuring wrestling, horse racing, and archery, are prominently celebrated. Although there have been influences from Russia and the West due to geopolitical relations, Mongolia’s culture has largely managed to preserve its unique Mongolian characteristics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Mongolia and China share complex historical and cultural connections, Mongolia is not part of China. It stands as a separate, sovereign nation. The term “Inner Mongolia” often leads to confusion, as it denotes an autonomous region within China and is distinct from the independent nation of Mongolia. The political and geographical demarcations between Inner Mongolia and the nation of Mongolia underline the latter’s independence from China, confirming that Mongolia is, indeed, not a part of China.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Mongolian the official language in Inner Mongolia?
While Mongolian is spoken in Inner Mongolia, Mandarin Chinese has become more dominant due to the region’s political affiliation with China. The Mongolian language is preserved and used, especially among ethnic Mongolians, but Mandarin Chinese is widely spoken and used in education, media, and public life.
What script is used in Mongolia and Inner Mongolia?
In Mongolia (Outer Mongolia), the Mongolian language, based on the Cyrillic script, is the official language. However, in Inner Mongolia, the traditional Mongolian script, which is written vertically, is used alongside Mandarin Chinese.
Is Mongolia part of China?
No, Mongolia is not part of China. It is an independent nation located in Central Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east, and west. It has been a sovereign nation since its independence from the Qing Dynasty in 1921.
What is Inner Mongolia and is it part of Mongolia?
Inner Mongolia, also known as South Mongolia, is an autonomous region within China. Despite its name, it is not part of the independent nation of Mongolia. It lies south of Mongolia and is home to a large Mongolian population, but is under the jurisdiction of the Chinese government.
What is the difference between Inner Mongolia and Outer Mongolia?
“Inner Mongolia” refers to an autonomous region within China, which is home to a significant Mongolian population and exhibits a blend of Chinese and Mongolian cultures. On the other hand, “Outer Mongolia” is the historical term for what we now call Mongolia. Unlike Inner Mongolia, Mongolia (Outer Mongolia) is a fully sovereign nation with its own government, economic systems, and social structures.
